Apple
- Promotional link: If you use this link to register, I will receive a portion of the revenue you pay. It won’t cost you more, so it’s a nice way to reward me for my work as well.
- Standard link: If, for some reason, you don’t want to support me, you can use this link to sign up, and that’s fine too. Moreover, the first 10 people who contact me can receive a special code that will give both of us a month of Raycast Pro.
- If you want to play your graph, navigate to it and switch your rotor to „Audio graph”. Then, swipe down to „Play the graph” and double tap. All going well you should hear your creation where the stereo panning determines X axis, Y axis is shown by a pitch change in the sound.
- You can also double tap and hold on the „Play graph” option. Doing that will put you in exploration mode, where you can drag your finger across the screen horizontally and feel the values under your finger. If you stop for a moment, VO will announce current axes and their values. Of course it is much nicer to use an iPad as you have much bigger working estate.
- You can use „Graph details” option to get a textual description of the graph. You can see whether data corelates, whether there are isolated values and what the general trend is.
- You can zoom in and out of the graph. Zooming in will give you a bit more detail on a smaller range of values while zooming out will give you a bird’s eye view. You will see more values but with less detail.
- You can always go back to default zoom level by selecting an appropriate option from the actions rotor menu.
- We make an
NSMutableStringfrom our swift String and immediately convert it to aCFMutableStringtype. This is because the methods we use later are the part ofCFMutableStringtype. Don’t worry about any performance implications here, the conversion between the two types is basically free. - We make a CFRange that spans throughout the length of the string. Apple likes to operate on ranges a lot while dealing with strings and you are going to see that a lot if you decide to dig deeper.
- Here lies the heart of our quest. The function takes four parameters in this case. The first parameter is the string to be transformed, the second parameter requires a few more words. We pass in the range we created in point 2 but we do something that is very rare in Swift, we pass the pointer to the range, not the range itself, hence the & symbol. The third parameter specifies the actual transformation we desire. In this case, we want to get the Unicode name of the symbol, but there are some more interesting options to choose from, for example, get the latin representation of Cyrillic letters, strip diacritics from strings, ETC. The fourth parameter specifies if we should perform the transformation in reverse (true). I couldn’t find any information online which transformations support reversing, so you need to experiment yourself. The return value is a bool. If it’s true, it means that our transformation succeeded.
- We finally print our string. If we see the Xcode’s log we see that we might want to prettify the string a little before using it in production, but the result is OK and it is very easy to make it production ready.
- We make a Data object out of our String type.
Datais just a byte buffer in the memory. We need this buffer in order to make a formatted string out of it in step 2. - We make our attributed string. The first parameter is the data object we want to use as an input. The second parameter is an array of options controlling the rendering process. Here we set our document type to be HTML, we can very easily render Markdown, for example. Actually we don’t even need the NSAttributedString
for that. We can use the third parameter to pass any additional attributes we might want, such as the author of the document. I left it atnil` here. As we can see, a relatively simple code can perform an actually useful operation on the string. Another thing is that it scales well, we could very easily make a simple HTML to markdown converter in literally few lin es of code. Would it be good? No but the point still stands. - accessibilitySpeechPunctuation: Allows to override default punctuation settings of VoiceOver. Useful when we need the user to know the punctuation, for example when reading some kind of code.
- accessibilitySpeechPitch: allows to speak a text with a voice that has a higher or lower pitch than our VoiceOver defaults.
- accessibilityTextHeadingLevel: allows to set a custom heading level for a text. Useful when presenting raw markdown to a user. It preserves heading navigation around the text.
- Open the Mail app.
- Focus the message you want to Drag.
- Focus the “Action” rotor.
- Select the “Drag” action and double tap it.
- Now, our element is in our hands. We can move it arround wherever we want.
- Open Reminders.
- Choose a list where you want to drop your item.
- In the “Actions” rotor, select “Drop on item” action.
Raycast: an ultimate macOS launcher
Introduction
I am a relatively new macOS user, having started to use the Mac seriously in 2021. Since then, I have tested countless apps—some better than others, some more useful, and some perfectly accessible with VoiceOver, while others were completely unusable with this screen reader. Coming from Windows, I had a set of favorite applications crucial to my workflow, one of which was Fluent Search, a great Windows launcher similar to Spotlight in the Apple ecosystem. While I had Spotlight on the Mac, it seemed poor compared to Fluent Search, especially with its awesome plugins, including my own YouTube Search. Thus, I began searching for alternatives and found two promising options: LaunchBar and Alfred. Long story short, I stuck with Alfred until a few weeks ago when I rediscovered Raycast.
Our First Meeting
I first heard about this launcher in early 2022. I enjoy watching videos about Mac apps, tips, and tricks, and one creator shared Raycast as an app he discovered and loved. He demonstrated examples that resonated with me, prompting me to think, “Yeah, Alfred isn’t good enough; let’s try Raycast.” I visited the website, downloaded the app, installed it, and began the configuration process. This was a huge disappointment for me, as the configuration process was far from optimal in terms of accessibility. Most controls were unlabelled, and when I was asked to choose which extensions to enable by default, I had no idea whether I was enabling or disabling an option. I had to use OCR to help me through the initial setup. After overcoming this hurdle, I was presented with the launcher’s main interface. Another disappointment, even bigger than the first, was that the program didn’t inform VoiceOver about the currently highlighted element. I had no idea what the active result was and had to navigate with VoiceOver to the table to see my selection. This felt much slower than Alfred and even Spotlight, which is slow by default unless you disable its most useful functions ;). However, I decided to press on, hoping to provide developers with the necessary feedback to improve the app’s accessibility. The tutorial Raycast offered was nice, clean, and, most importantly, extremely accessible. This aspect remains present in the app; the accessibility is inconsistent—sometimes it’s best in class, while at other times, I need to rely on OCR for assistance. I completed the tutorial, played around for a few more minutes, wrote a polite email outlining the issues, uninstalled the app, and returned to my boring life.
New Mac, New Me
Fast forward to early December 2024. I got a brand new Mac Mini M4 Pro and started configuring it. I am making backups as simple backups, not images to restore a new computer. The reasons behind this decision are beyond the scope of this article, but one advantage is that I can go through my setup and determine what I really need and what I can live without. This saves money, time, and disk space while allowing me to discover new things and reflect on my working style in greater detail. When faced with the task of reinstalling Alfred, I suddenly remembered that many of the workflows I used were broken, that I had forgotten how to grant permissions to some of them, and that it would be a greater hassle than I initially thought. I decided to check how things were on Raycast’s end. After some searching, I discovered this article written by a blind macOS power user, just like me. It is short and, as its name implies, showcases only the author’s first impressions. According to their words, the setup process had improved for VoiceOver users. “Great,” I thought, and I downloaded Raycast once again.
Second Try and I’m In
The initial setup process has significantly improved for blind users. Some buttons are now labeled, and it is possible to choose the first extensions. However, the biggest issue remains: the selected result is still not automatically announced by VoiceOver. Despite this, Raycast has replaced at least five apps I used as my daily drivers. Below, I will outline my most important workflows with Raycast.
Calculator
Raycast uses the engine of Soulver, a powerful natural language calculator for macOS. It can perform simple math operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, but that’s just the beginning. My most-used function is currency conversion. By typing a simple expression, such as “1 eur pln,” I can get a nearly instant result straight from the server. Even better, I can pin my favorite calculations to the top of the list, so when I access the calculation history next time, I see the updated value. One downside regarding currency conversions is that it shows results only to the second decimal place. While this is fine for normal use, as someone who occasionally engages in currency trading, I find it a bit limiting. The calculator can also perform time zone conversions and tell you when next Monday is. It has replaced Soulver for me, as it is much quicker to access for my needs.
Clipboard History
Another feature I can’t live without is clipboard history. Previously, I used another app for clipboard management, but I found its subscription too expensive for my tight budget, so I switched to Raycast as a full-fledged clipboard manager. I assigned a hotkey to open the clipboard history—CTRL+V. I land directly on a text box where I can type my search query. I can choose a result from a table to the right of the box, and that’s it. I can view some metadata about the item, such as the app it comes from and the number of times I’ve used it. One downside compared to Copy ‘em is that I see no way to filter items by source app. I relied heavily on this function for copying from Safari and other apps, so now I have to remember what I’m searching for. In spite of this little limitation I find Raycast to be much sleeker than Copy ‘em, that’s another one down.
Menu Bar Searching
Deep in the Raycast settings interface, I found a command called “Menu Search,” which, as the name implies, lets me search the menu bar of the current frontmost application with ease. This function replaced an app I previously used called Paletro. While Paletro still has some advantages, such as the ability to disable the command palette in certain applications or better overall accessibility, as we say here in Poland, “free is always an honest price.” Plus, Raycast has a streamlined UI, so I don’t have to think about whether I am searching the menu or YouTube for my favorite Christmas song.
Have I Mentioned Extensions?
Raycast is powerful out of the box, but what makes it truly exceptional is its extension system. It allows third-party developers to integrate new functions into Raycast, enabling us, the users, to incorporate these features into our workflows. Some extensions I use daily include one that allows me to see my Wise balance from Raycast, change audio devices on the fly, and manage Apple Reminders. Oh, and there’s an extension that helps me find cool Hearthstone decks, as I’m addicted to that game. What’s great about these plugins is that they are as streamlined as the main app. We still have the Command+K action panel, CMD+Return to submit forms, and that simple, tabular interface. The Raycast Store offers countless extensions, ranging from simple one-command utilities to complex ones that behave almost like separate apps.
Epilogue
This was meant to be a quick overview of Raycast from the perspective of a blind power user of the Mac. In summary, while it may not be as accessible as other macOS launchers, it is far more powerful, robust, and streamlined, making it an easy choice for me. The countless available extensions, beautifully integrated AI support, shareable snippets across your organization, and literally hundreds of other features I haven’t even touched on in this article have won my heart.
Raycast is mostly free, but if you like it and want to support their work while gaining additional benefits, you can join Raycast Pro. I wish to be honest with my readers, so I offer you two ways to join:
Using Apple Notes as an accessible graphing calculator
Starting with the basics
With the release of their latest batch of operating systems Apple made some substantial updates to both the Calculator and Notes app. I am not even saying about bringing an official Calculator to the iPad for the first time but more a feature called Math Notes which lets us, as the name implies create notes with math expressions inside them. For starters, we can define variables and perform calculations on those variables.
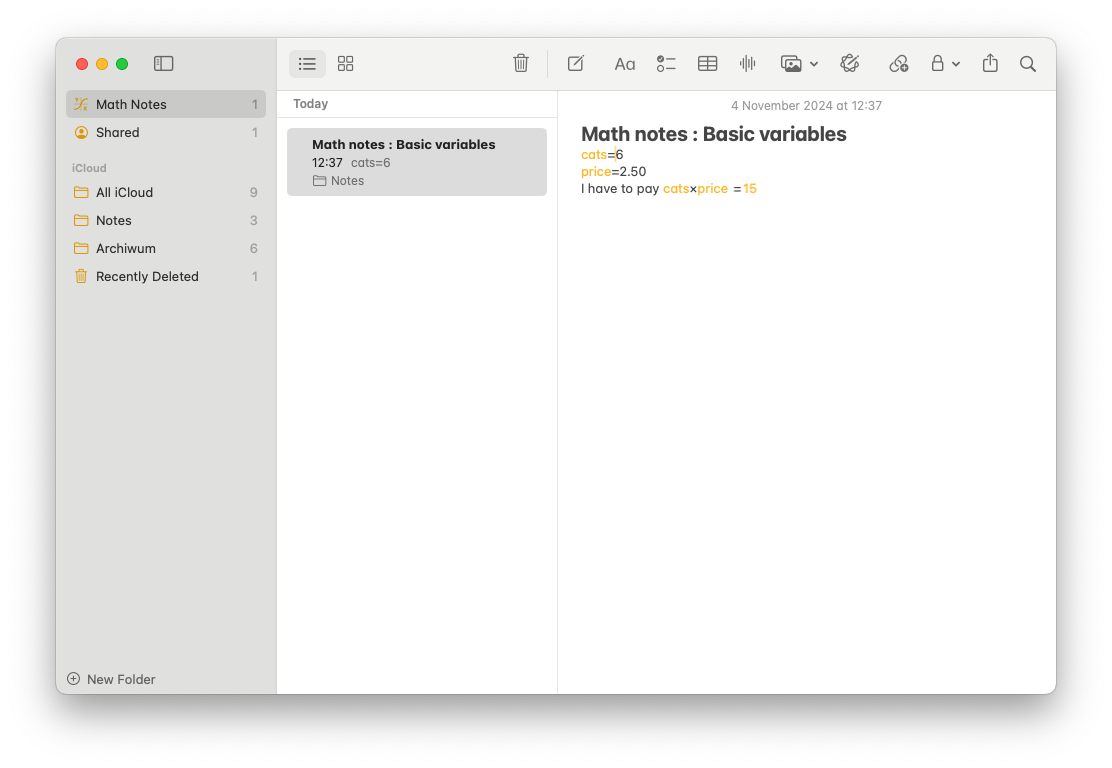
The best thing is that there’s no magic in all of this. You can use natural language to describe your variables. There are no hard rules of naming them like in programming.
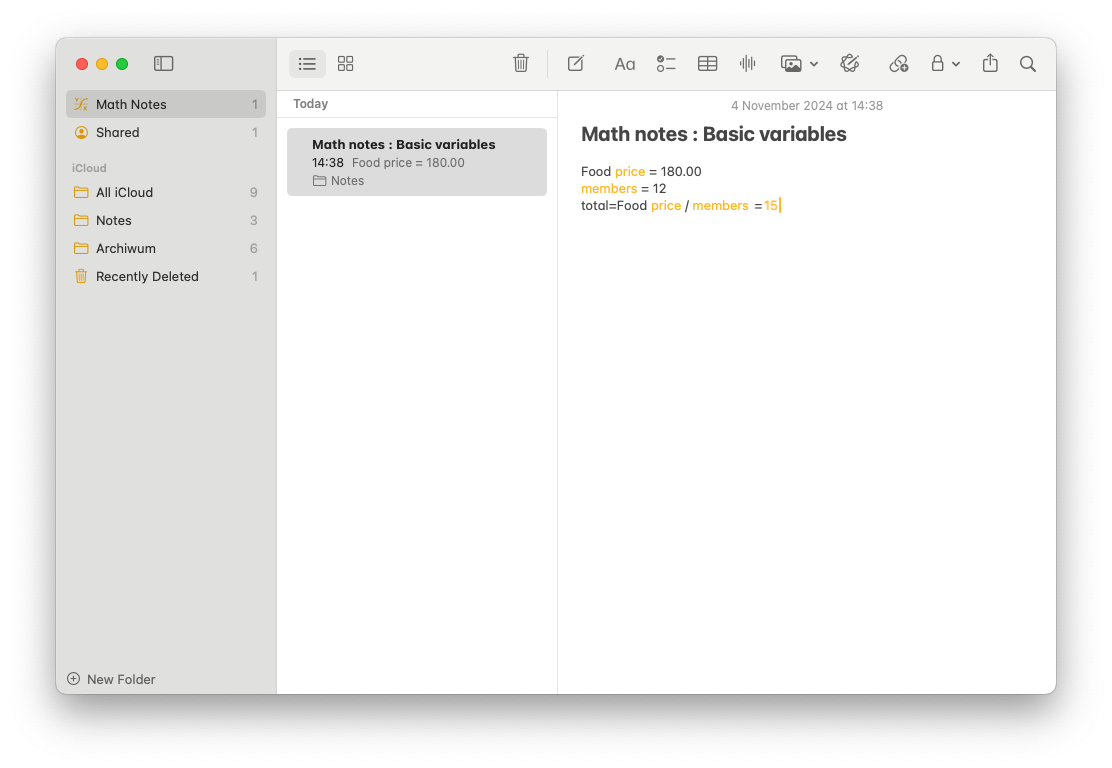
However that’s not everything. We can use the exact same app to graph equations.
If we type, for example and then use rotor menu on our iPhone, we can find an option „Insert graph”. Double tapping it will insert a graph next to our expression.
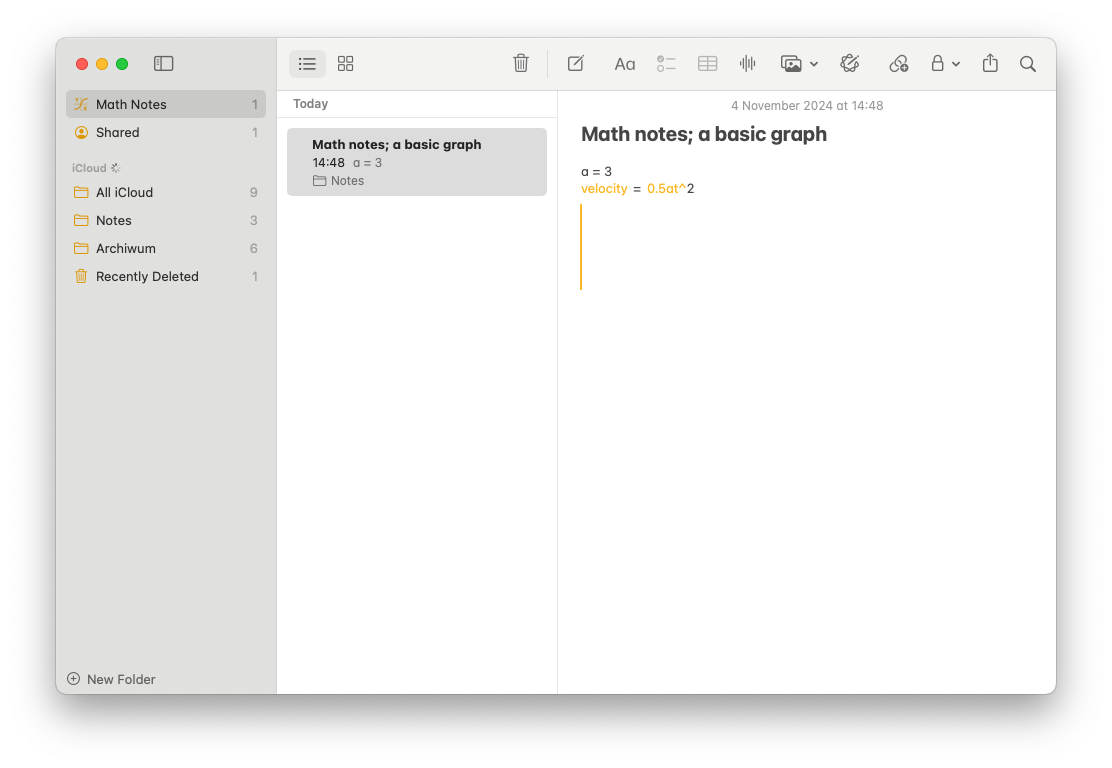
For all fans of the Mac out there I have some bad news. For some reason it is very hard, if not impossible to insert a graph with VoiceOver. My tip is to write out your equation on a Mac and then use an iPhone to insert a graph. Then, going back to the Mac you can explore the graph as you would do with any Swift chart graph.
Exploring our graphs with VoiceOver
When the system finishes drawing the graph we can use standard VoiceOver’s commands to explore it. Of course some graphs can be infinite, hence only a part of the graph is shown at the same time.
How does it relate to other accessible graphing tools?
Over the years we had some accessible graphing calculators, some more sophisticated than the others. The most obvious choice was Desmos which I still consider to be an excellent piece of software. However its obvious drawback is that it requires constant Internet connection to function which can easily rule it out as a tool at school or university in some situations. Then we had some prototypes such as this but its Windows only, or the new kid on the block written in Go. The problem with those tools is that they have a pretty high entry level and I can’t imagine myself at a mainstream high school with a final exam approaching trying to figure out why the hell a given piece of software doesn’t want to compile.
Epilogue
I hope you found this article useful and I hope even more that thanks to it you won’t struggle at math as much as I did. Let’s make math accessible to everyone!
Some interesting things we can do with strings in Swift
Today I want to discuss strings in Swift
Hello everyone. I am trying to reinforce my knowledge of some interesting topics by writing about them./ I like to write as this gives me an introspection into my thought process, allows others to get possibly interested in a topic and learn from me, and allows me to learn from much better people than myself. If I have time, I will try to write those articles here. Some of them might be blind-related and others will be about mainstream programming. Keep in mind that I am not a programming God, I might make errors and feel free to correct me.
What are we talking about today?
Everyone, even the most novice programmer is using strings. They allow us to represent text in our programs, and text is something that drives our everyday life in many ways. We read articles, write messages to our loved ones and make programs, of course. So we could think that strings are rather uninteresting, sugarcoated array of characters, for example C-Style strings are just an array of characters. Even if an underlying implementation is somewhat different there’s a pretty easy way to use strings just like a char array. For example in C# we could do something like
string test = "Hello, world!";
char test2 = test[2]; // returns 'l' since that's the 3rd character in our string.
That trick works in many languages, including Python. But in Swift, the language used mostly in the world of Apple we need to give this seemingly simple task a little bit more thought. Let me show you:
var a = "ABCDEF"
var b = Array(a)
print(b[2])
It is still a simple task but as you can see, we first need to explicitly convert our string to an array of characters. By the way I recommend you do one more test for yourself. What result will be returned by the following statement?
print(type(of: b[2]))
This whole mess is because Swift strings are fully Unicode-aware. If you have played some Chinese, Japanese, Russian ETC games and you had to use Locale Emulator you have seen the lack of proper Unicode support in practice. The problem with Unicode though is that some characters, especially emoji might be composed of more than one Unicode scalars. A scalar is a basic unit in Unicode, for example some emoji have skin tones which are represented by a scalar. A skin tone without a thumbs up, for instance does not make much sense, but if we allowed for using a Swift string like a char array, we could, in theory get an unprintable character that makes no sense. What I want to say here is that because Swift makes some simple things harder for us, we get many more more grant, useful processes simplified since the language does a lot on our behalf.
However Swift strings are even more powerful than that, and there are many APIs from Apple that allows us to work with them in a variety of interesting ways. By the way here the border between a SwiftString and NSString blurs. I know that my wording is not entirely correct, but it is correct enough for our purposes. If you want to read more, there are websites such as NSHipster that will explain the nuances much better than I ever could.
Get a name of an Emoji
Have you ever wondered how VoiceOver knows all the names of various Emoji you encounter in your day to day iPhone usage? There’s just a database stored somewhere which has all the names of those, and we can get them in our code as well. Let me show you an example.
var emoji = "☭"
/*1*/let coreFoundationString = NSMutableString(string: emoji) as CFMutableString
/*2*/var range = CFRangeMake(0, CFStringGetLength(coreFoundationString))
/*3*/CFStringTransform(coreFoundationString, &range, kCFStringTransformToUnicodeName, false)
print(coreFoundationString)
This code is pretty long and convoluted as is very much non-swift (Welcome to the world of Apple APIs) but after breaking it down it isn’t that bad. And if you were to do many such operations, you would probably abstract it in a more Swifty way anyway so there’s no problem.
Render HTML in our user interface without WKWebView
HTML is very popular when we deal with data from the Internet. Sometimes we need to render it inline in our user interface and we don’t want to spawn a browser for that. Here a type called NSAttributedString come into play. It is a crazily powerful type that is basically a string, but with additional metadata allowing us to perform some advanced operations with relative ease. Let me show you how we can render HTML inline, useful for example when making labels for elements.
This code snippets has some SwiftUI and UIKit code in it but we don’t care about it. The reason I included it is completeness.
var text: String
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> UILabel {
let label = UILabel()
DispatchQueue.main.async {
/*1*/ if let data = text.data(using: .unicode) {
/*2*/ if let attrString = try? NSAttributedString(data: data, options: [.documentType: NSAttributedString.DocumentType.html], documentAttributes: nil) {
label.attributedText = attrString
}
}
}
return label
}
The code is long but we have only 2 points of interest.
Control how VoiceOver reads strings
We are still staying in the world of NSAttributedString. There are some attributes which make it possible to somewhat control how the string is spoken by VoiceOver. Let me show you a very simple example, taken from Orion Gomez’s audiogame utilities for Swift repository.
let attributedLabel = NSAttributedString(string: text, attributes: [NSAttributedString.Key.accessibilitySpeechQueueAnnouncement: true])
This is how we make queued announcements. But there are many more accessibility attributes of which some I will discuss below.
Epilogue
This is my first serious article about programming. It cost me a lot to write it because I am very stressed about the reception. I hope that at least one person will benefit from it.
Accessible Drag & Drop on iOS with VoiceOver
Introduction
Drag & Drop is a function that’s with us almost from the beginning of our digital, GUI-oriented world. With Drag & Drop we can drag files from our File Explorer to our mail client. We can drag audio/video files to our media editor. Or, most importantly, we can drag cat photos to the conversation window we have opened with our significant one. However there’s a myth going arround that states that Drag & Drop cannot be used by blind people. And while the matter is more complicated on desktop computers, today I am going to debunk this myth by showing you how to perform accessible D & D straight from our iPhone.
What can be dragged?
In iOS, most stock apps offer us the Drag & Drop functionality of sorts. We can drag files to Messages, messagest o files, safari tabs to messages ETC. However in today’s example I am going to show you how can you link your E-Mails with the Reminders app in order to make the important E-Mails stay in the spotlight.
Recipe
Now, our Reminder will be created, and the Mail will be put in the reminder as a link.
I hope you have found this useful. In case of questions, feel free to contact me! I am happy if I hear from you.